Draw the product of the complete hydrogenation of ethyne. – Embarking on an exploration of the complete hydrogenation of ethyne, this article delves into the intricacies of this chemical process, unraveling its mechanism, product formation, and diverse applications. Prepare to delve into a realm where scientific precision meets industrial significance, as we unveil the fascinating world of ethyne hydrogenation.
Hydrogenation, a chemical reaction involving the addition of hydrogen to a compound, plays a pivotal role in transforming ethyne into a valuable product. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of the complete hydrogenation of ethyne, encompassing its mechanism, product formation, properties, applications, and safety considerations.
Product of Complete Hydrogenation of Ethyne
The complete hydrogenation of ethyne is a chemical reaction that adds two hydrogen atoms to the triple bond, converting it into a single bond. This process is typically carried out in the presence of a catalyst, such as nickel or palladium.
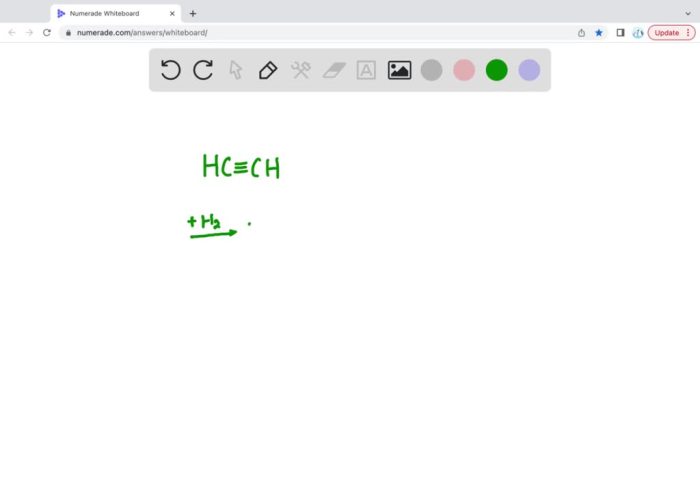
The chemical equation for the complete hydrogenation of ethyne is:
C2H 2+ 2H 2→ C 2H 6
The product formed during this reaction is ethane, a saturated hydrocarbon with a single bond between the two carbon atoms.
Mechanism of Hydrogenation: Draw The Product Of The Complete Hydrogenation Of Ethyne.
The hydrogenation of ethyne is a catalytic process, meaning that it requires a catalyst to proceed. The catalyst provides a surface on which the reactants can adsorb and react.
The mechanism of ethyne hydrogenation involves the following steps:
- Ethyne adsorbs onto the surface of the catalyst.
- A hydrogen molecule adsorbs onto the surface of the catalyst.
- The hydrogen atoms from the hydrogen molecule are transferred to the ethyne molecule, forming a double bond.
- The double bond is further hydrogenated to form a single bond.
- The ethane molecule desorbs from the surface of the catalyst.
The catalyst facilitates the reaction by providing a surface on which the reactants can adsorb and by lowering the activation energy of the reaction.
Properties and Applications of the Product
Ethane is a colorless, odorless gas at room temperature. It is highly flammable and has a boiling point of -88.6°C.
Ethane is used as a fuel and as a feedstock for the production of other chemicals, such as ethylene and polyethylene.
Examples of products that utilize ethane include:
- Plastics
- Synthetic fibers
- Solvents
Comparison with Other Hydrogenation Reactions
The hydrogenation of ethyne is similar to the hydrogenation of other unsaturated hydrocarbons, such as alkenes and alkynes.
However, there are some key differences between the hydrogenation of ethyne and the hydrogenation of other unsaturated hydrocarbons.
- The hydrogenation of ethyne is typically carried out at lower temperatures than the hydrogenation of other unsaturated hydrocarbons.
- The hydrogenation of ethyne is more selective than the hydrogenation of other unsaturated hydrocarbons.
The selectivity of the hydrogenation of ethyne is due to the fact that the triple bond in ethyne is more reactive than the double bond in alkenes and the single bond in alkynes.
Safety Considerations
The hydrogenation of ethyne is a potentially hazardous reaction.
The following safety precautions should be taken when carrying out this reaction:
- The reaction should be carried out in a well-ventilated area.
- The reactants and products should be handled with care.
- Proper protective equipment, such as gloves and goggles, should be worn.
Popular Questions
What is the product of complete hydrogenation of ethyne?
The product of complete hydrogenation of ethyne is ethane, a saturated hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C2H6.
What is the role of a catalyst in the hydrogenation of ethyne?
A catalyst, typically a metal such as palladium or platinum, facilitates the hydrogenation process by providing an active surface for the reaction to occur.
What are the industrial applications of the product formed by ethyne hydrogenation?
The product of ethyne hydrogenation, ethane, is used in various industrial applications, including fuel production, plastics manufacturing, and as a feedstock for other chemical reactions.