All of the following are basic mindfulness skills except: This article delves into the realm of mindfulness, exploring the fundamental skills that cultivate present-moment awareness. While mindfulness offers a plethora of benefits, it is crucial to distinguish between basic and non-basic skills to optimize the practice.
This guide will shed light on the essential elements of mindfulness, unraveling the nuances that differentiate basic from non-basic skills. By understanding this distinction, individuals can tailor their mindfulness practice to their specific needs and aspirations.
Basic and Non-Basic Mindfulness Skills: All Of The Following Are Basic Mindfulness Skills Except

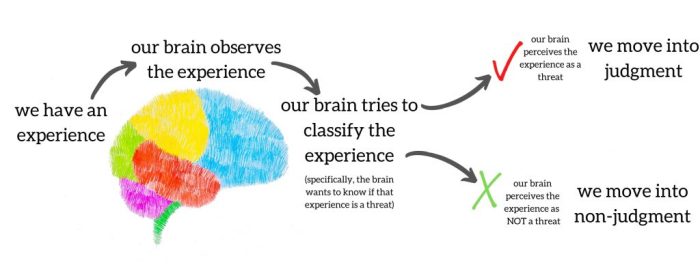
Mindfulness is a practice that involves paying attention to the present moment without judgment. It has been shown to have a number of benefits, including reducing stress, improving focus, and increasing compassion. There are a number of basic mindfulness skills that can be learned and practiced to help develop mindfulness.
These skills include:
- Body scan meditation
- Breath awareness meditation
- Mindful walking
- Mindful eating
These skills are considered basic because they are relatively simple to learn and can be practiced in everyday life. However, there are a number of other skills that can be considered non-basic mindfulness skills. These skills are typically more complex and require more practice to develop.
Non-Basic Mindfulness Skills, All of the following are basic mindfulness skills except
Some of the non-basic mindfulness skills include:
- Mindful listening
- Mindful speaking
- Mindful movement
- Mindful self-compassion
These skills are not considered basic because they require a deeper level of understanding and practice. For example, mindful listening requires the ability to be present and attentive to what another person is saying without judgment. Mindful speaking requires the ability to communicate in a way that is clear, compassionate, and honest.
Mindful movement requires the ability to be aware of the body and its movements without judgment. Mindful self-compassion requires the ability to be kind and understanding towards oneself.
Examples of Non-Basic Mindfulness Skills
Here are some specific examples of activities or techniques that fall outside the realm of basic mindfulness skills:
- Mindful listening:Paying attention to what someone is saying without judgment or interruption. Trying to understand their perspective and feelings.
- Mindful speaking:Speaking in a way that is clear, compassionate, and honest. Avoiding gossip or hurtful language.
- Mindful movement:Paying attention to the body and its movements without judgment. Noticing sensations, tension, and relaxation.
- Mindful self-compassion:Being kind and understanding towards oneself. Accepting mistakes and shortcomings without self-criticism.
These examples illustrate how non-basic mindfulness skills differ from basic mindfulness practices. Basic mindfulness skills are focused on developing present moment awareness, while non-basic mindfulness skills are focused on developing specific qualities and abilities that can be applied in everyday life.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the primary focus of basic mindfulness skills?
Basic mindfulness skills center on cultivating present-moment awareness through techniques such as focused breathing, body scans, and mindful observation.
How do non-basic mindfulness skills differ from basic skills?
Non-basic mindfulness skills extend beyond present-moment awareness, incorporating elements such as self-compassion, acceptance, and emotional regulation.
Can mindfulness skills be tailored to individual needs?
Absolutely. Understanding the distinction between basic and non-basic skills allows individuals to customize their mindfulness practice, selecting techniques that resonate with their specific goals and aspirations.